Acromioclavicular Joint AC Joint in shoulder, AC Joint Pain

The acromioclavicular ligament is part of the acromioclavicular joint. It is divided into two parts: superior and inferior: The Superior Acromioclavicular Ligament (ligamentum acromioclaviculare).—This ligament is a quadrilateral band, covering the superior part of the articulation, and extending between the upper part of the acromial end of the clavicle and the adjoining part of the upper.
Shoulder Joint Ligaments
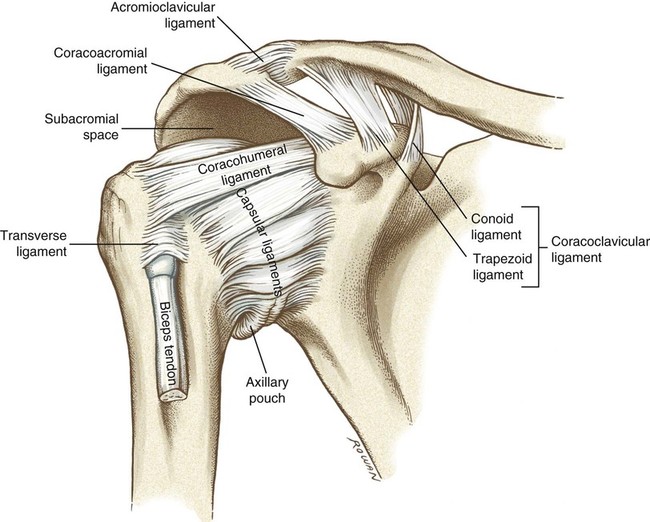
Una parte de las fibras del músculo trapecio se fusionan con este ligamento, sosteniendo la cápsula articular desde su lado superior. De manera similar, el ligamento acromioclavicular inferior conecta las superficies inferiores del acromion y la extremidad acromial de la clavícula. Es más delgado que su contraparte superior y puede.
The Acromioclavicular Joint Structure Movement TeachMeAnatomy
Da mesma forma, o ligamento acromioclavicular inferior liga as superfícies inferiores do acrômio e da extremidade acromial da clavícula. É mais fino do que o seu homólogo superior e pode sofrer perfurações com a idade. Tem particular importância em indivíduos cujas superfícies articulares da articulação acromioclavicular não são.
Acromioclavicular Dislocation Doctor Matthieu Meyer
The AC joint represents a complex articulation between the distal clavicle and the anteromedial aspect of the acromion and plays an important role in the coordination shoulder motion and force transmission between the shoulder girdle and the axial skeleton (Fig. 7.1) [ 1, 2 ]. Because the clavicle is linked to the acromion, three-dimensional.
Articulacin Acromioclavicular

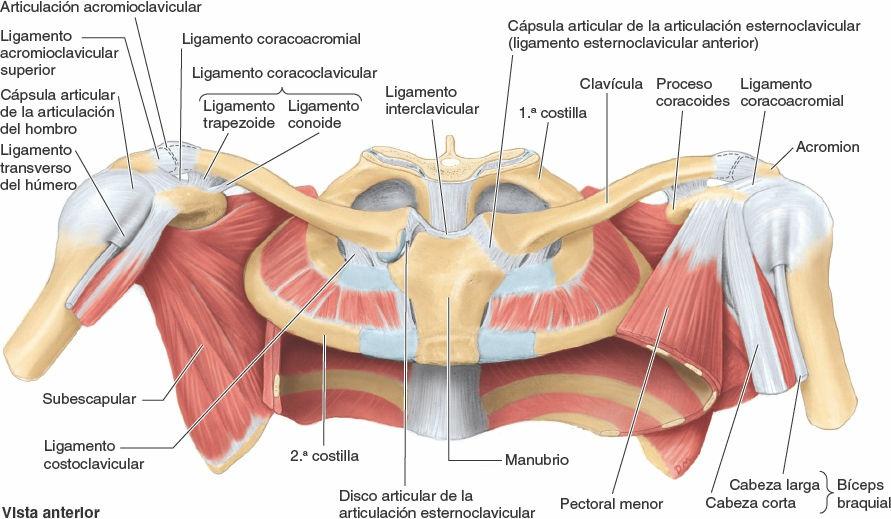
There are three types of disc 8-11: A weak, synovium-lined joint capsule is attached to the articular margins and is reinforced superiorly by blending fibers of the trapezius muscle 6. The acromioclavicular joint space measures 1-6 mm (females) and 1-7 mm (males), decreasing with age 12 . The acromioclavicular joint is one of the letter joints 13.
10. Articulaciones del Miembro Superior Enfermería
AC joint. Osteology. the AC joint is a diarthrodial joint. fibrocartilaginous intraarticular disc is located between the osseous segments. Motion. majority of motion is from the bones, not through the joint. clavicle rotates 40-50° posteriorly with shoulder elevation. 8° of rotation through AC joint. remainder from scapular rotation and.
Acromioclavicular Joint Anatomy Earth's Lab

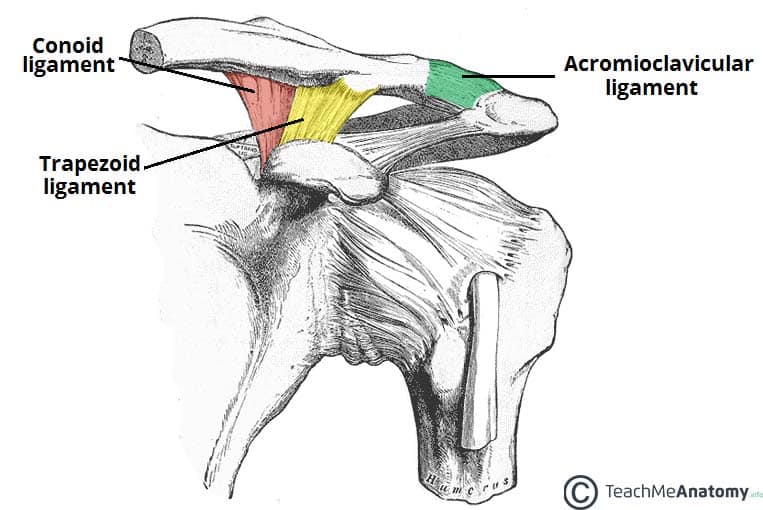
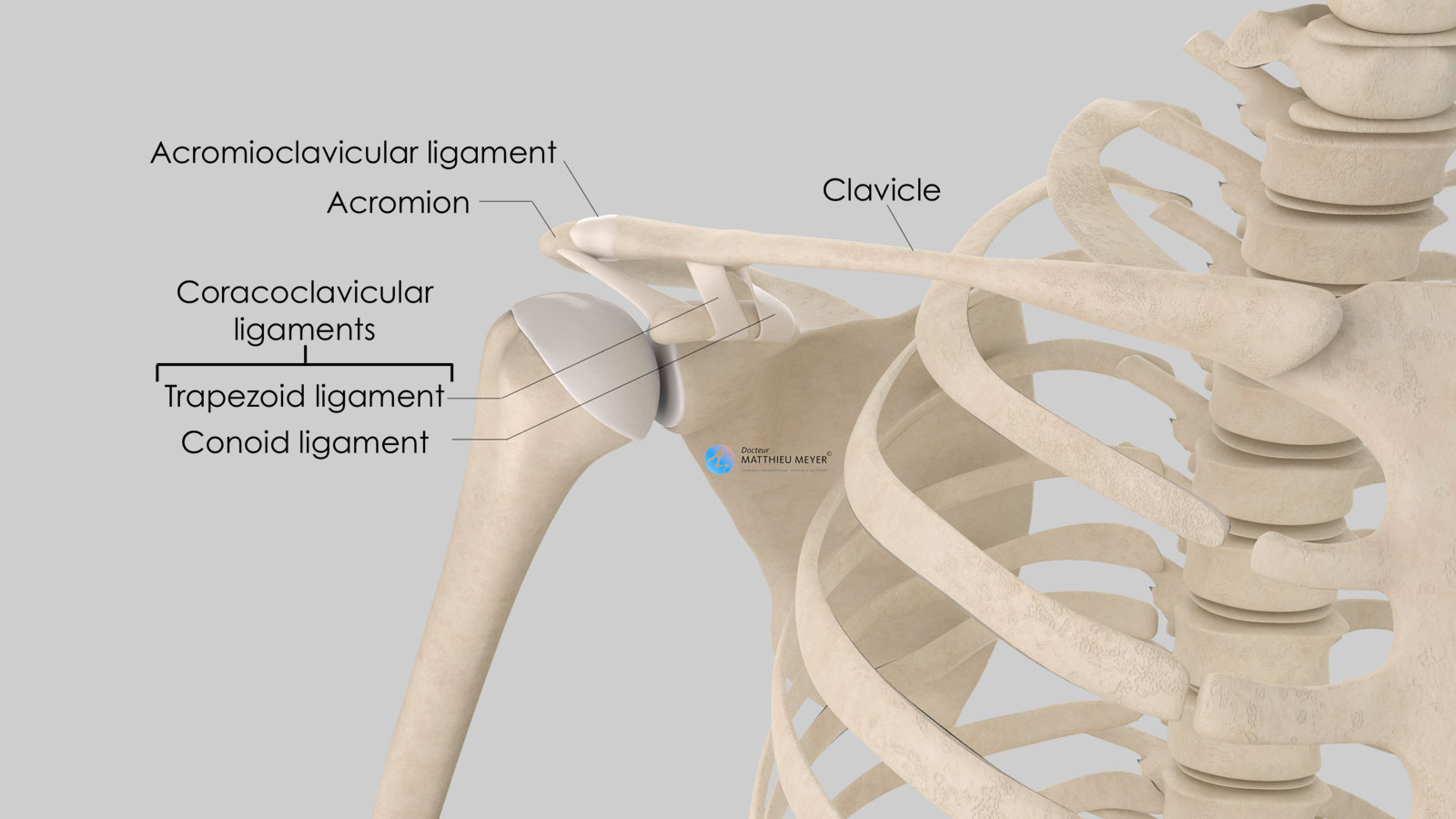
The coracoclavicular (CC) ligament serves as the primary support for the acromioclavicular (AC) ligament. Together, these 2 ligaments stabilize the acromioclavicular joint, which is one of the major shoulder joints. To better understand the role of the coracoclavicular ligament, it is necessary to understand the anatomy of the acromioclavicular joint. The acromioclavicular joint serves a vital.
LIGAMENTOS DEL HOMBRO Dolopedia

The acromioclavicular ligament is a ligament of the shoulder that surrounds the acromioclavicular (AC) joint between the acromion on the top of the scapula and the clavicle, or collarbone. It is divided into two parts: the superior acromioclavicular ligament and the inferior acromioclavicular ligament. Both parts of the ligament are made of.
PATHOLOGY OF THE ACROMIOCLAVICULAR JOINT (AC) ALAI

Background. The selection of the ideal reconstruction technique to treat acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) dislocations is still being discussed [].In biomechanical studies, anatomical reconstruction of the coracoclavicular (CC) ligaments has demonstrated superior primary stability and load to failure similar to native ligaments compared to non-anatomical reconstructions [2-4].
coracoacromial ligament Google Search Shoulder anatomy, Joints anatomy, Shoulder joint anatomy

Anatomical Relations. The acromioclavicular ligament joins the upper aspect of the acromion of the scapula to the acromial (or lateral) aspect of the clavicle. Inferiorly, the ligament is thin. It provides an attachment for the articular disc of the acromioclavicular joint.
Articulacin Acromioclavicular

Acromioclavicular joint (Articulatio acromioclavicularis) The acromioclavicular (AC) joint is the articulation between the two bones of pectoral girdle; the clavicle and scapula.It is a plane synovial joint, with flat articular surfaces which are approximately the same in size.. Since there are no muscles that act directly on this joint, the movements within it are entirely passive.
Acromioclavicular (AC) joint Anatomy, function Kenhub
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13126/gP6Q4sJT8YGVD3NulKHNKg_Acromioclavikular_01.png)
The acromioclavicular joint is an important component of the shoulder girdle; it links the axial skeleton with the upper limb. This joint, a planar diarthrodial articulation between the clavicle and the acromion, contains a meniscus-like fibrous disk that is prone to degeneration. The acromioclavicular capsule and ligaments stabilize the joint in the horizontal direction, while the.
Articulación acromioclavicular Dolopedia

Biomechanically, the superior ligament was demonstrated as stronger than the inferior AC ligament, thus having an important role in controlling rotational and horizontal stability [2, 4, 5]. However, as the inferior ligament is often much thinner, anatomically, it should be considered more difficult to consistently detect and measure [3,4,5,6].
Anatomía del hombro, manguito rotador, funcional, imagenes, ligamentos y articulação

Abstract. Acromioclavicular (AC) joint injury is a frequent diagnosis after an acute shoulder trauma - often found among athletes and people involved in contact sports.This injury occurs five times more frequently in men than in women, with the highest incidence in the 20- to 30-year-old age group. Patients usually complain of pain and.
Articulacin Acromioclavicular
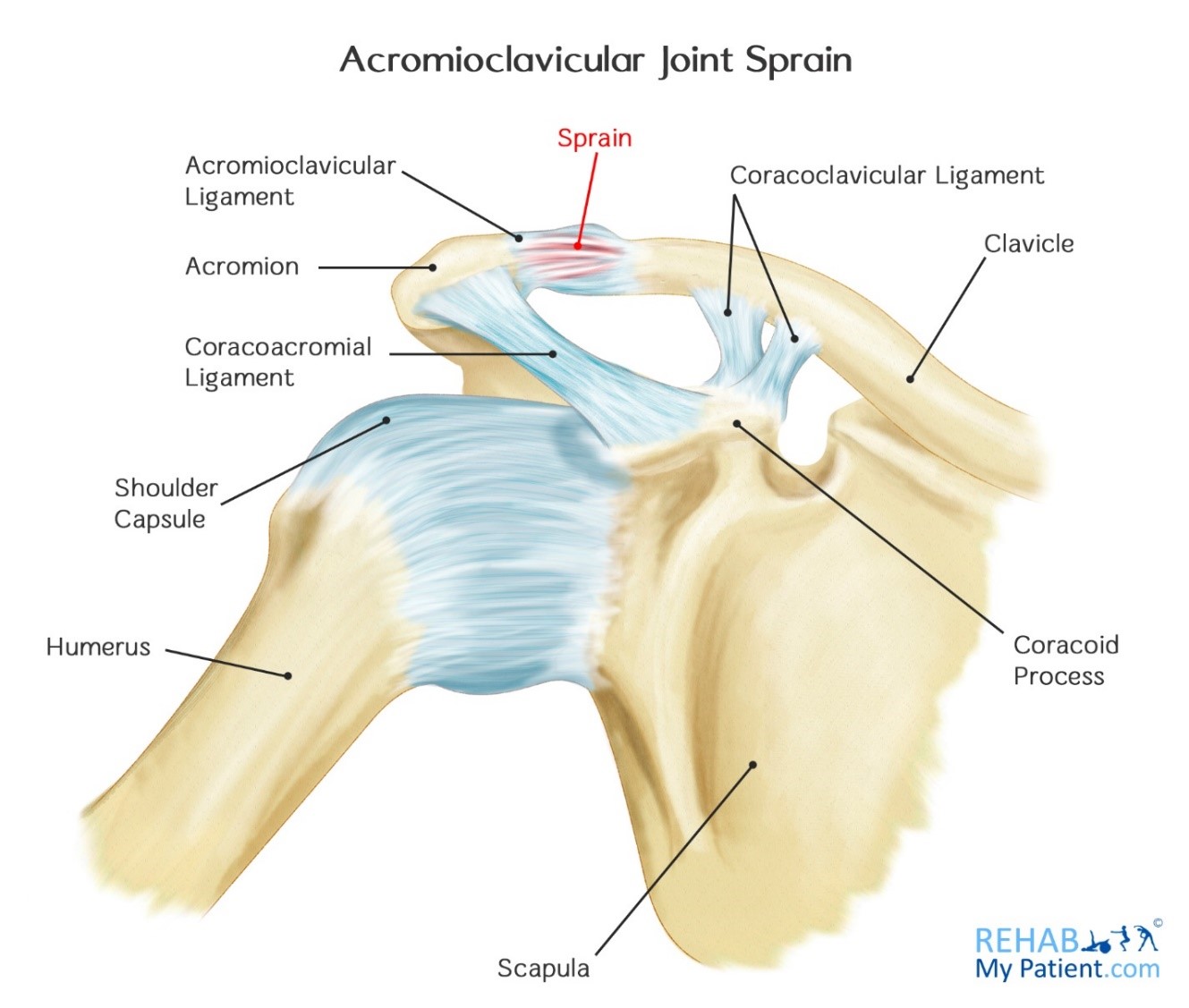
Superior acromioclavicular ligament. This ligament is a quadrilateral band, covering the superior part of the articulation, and extending between the upper part of the lateral end of the clavicle and the adjoining part of the upper surface of the acromion . It is composed of parallel fibers, which interlace with the aponeuroses of the trapezius.
Anatomy of the sternoclavicular and acromioclavicular joints Osmosis

The trapezoid ligament is quadrilateral. It is attached to the superior aspect of the anterior border of the base of the coracoid process and extends in a posterosuperolateral, roughly straight course to the trapezoid line in the inferior surface of the clavicle (Figs. 1B and 1C).The trapezoid ligament is the primary restraint against posterior clavicular displacement [] and also provides.